The growing interest in sustainable living has placed solar power at the forefront of renewable energy solutions for homeowners. By harnessing energy directly from the sun, solar technology offers a practical way to reduce both your environmental footprint and monthly electricity costs. This guide explores how solar energy can transform your home into an eco-friendly haven while providing significant long-term savings.
Understanding Solar Energy: The Basics
Solar power harnesses energy from the sun and converts it into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) technology. When sunlight hits solar panels, it creates an electric field across the layers of silicon cells, causing electricity to flow. This clean energy source produces no emissions during operation, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
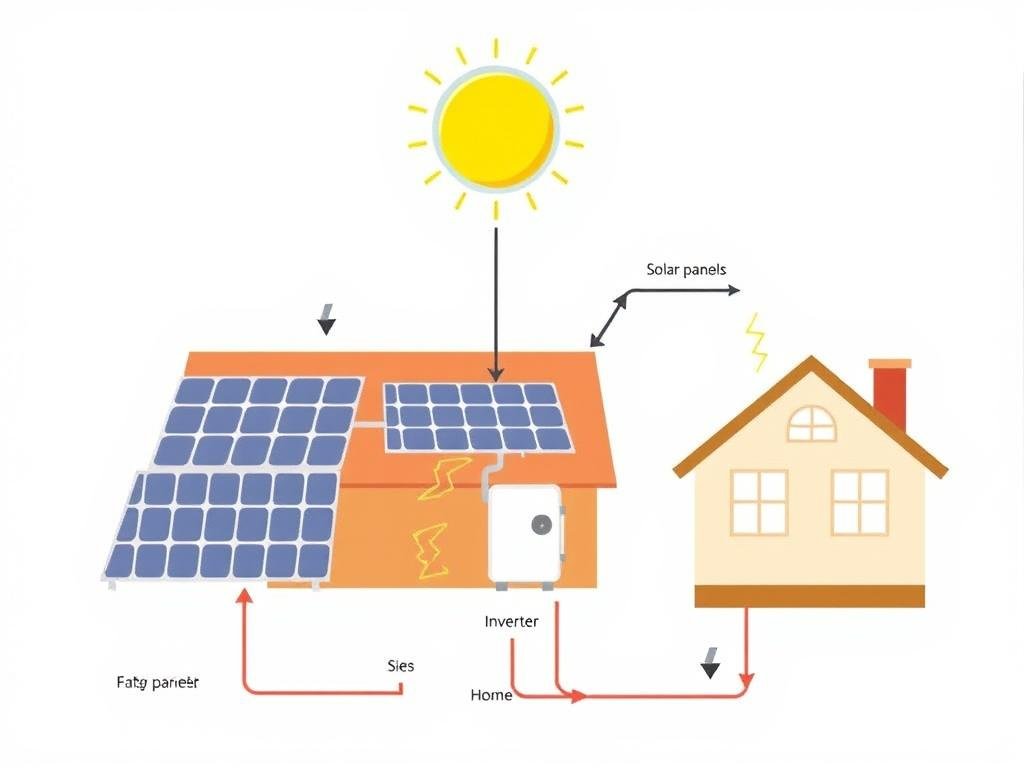
There are two primary solar technologies available for residential use:
Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
These systems use solar panels installed on rooftops or ground-mounted arrays to convert sunlight directly into electricity. PV systems are the most common choice for residential solar installations, offering a reliable and low-maintenance solution for homeowners.
Solar Heating and Cooling
These systems collect thermal energy from the sun to heat water or provide space heating and cooling. While less common than PV systems, they can be an efficient way to reduce energy costs in homes with high water heating demands.
5 Key Benefits of Solar Panel Installation
Transitioning to solar power offers numerous advantages beyond just reducing your carbon footprint. Here are five significant benefits that make solar energy an attractive option for environmentally conscious homeowners:

1. Significant Reduction in Electricity Bills
Solar panels generate free electricity during daylight hours, dramatically reducing your reliance on grid power. Depending on your system size and energy consumption, you could save 50-90% on your monthly electricity bills. In areas with net metering policies, excess energy produced can be fed back to the grid, potentially earning you credits on your utility bill.
2. Decreased Carbon Footprint
By generating clean electricity from the sun, a typical residential solar system can eliminate 3-4 tons of carbon emissions annually—equivalent to planting over 100 trees each year. This significant reduction in greenhouse gases helps combat climate change and reduces air pollution in your community.
3. Energy Independence
Solar power reduces your vulnerability to rising utility rates and power outages. When paired with battery storage, solar systems can provide electricity during grid failures, ensuring your essential appliances remain operational. This energy security becomes increasingly valuable as extreme weather events become more common.
4. Increased Home Value
Research shows that homes with solar installations sell faster and for higher prices than comparable non-solar homes. A study found that buyers are willing to pay a premium of approximately $15,000 for a home with an average-sized solar array. This investment not only pays for itself in energy savings but also in property value appreciation.
5. Low Maintenance Requirements
Modern solar panels are built to withstand harsh weather conditions and typically come with 25-30 year warranties. With no moving parts, maintenance is minimal—usually just occasional cleaning and an annual inspection. This reliability makes solar one of the most hassle-free renewable energy options available to homeowners.
How Solar Energy Reduces Your Electricity Bill
Understanding the financial benefits of solar power helps homeowners make informed decisions about this investment. Here’s how solar panels translate into real savings on your monthly electricity costs:
Immediate Reduction in Grid Electricity Usage
From the moment your solar system is activated, you’ll begin generating your own electricity. During daylight hours, your home will draw power from your solar panels instead of the grid, immediately reducing your purchased electricity. The amount saved depends on your system size, sun exposure, and energy consumption patterns.
Net Metering Benefits
Many utilities offer net metering programs, which credit you for excess electricity your system produces and feeds back to the grid. These credits can offset the cost of power drawn from the grid when your system isn’t producing (such as at night). In some areas, you can even carry these credits forward to future bills, maximizing your savings throughout the year.

Protection Against Rising Utility Rates
While electricity rates have historically increased by about 2-3% annually, solar panel owners lock in their energy costs when they install their system. This insulation from rate increases becomes more valuable over time, significantly enhancing the long-term savings of going solar.
The average American household can save between $10,000 and $30,000 over the lifetime of a solar panel system, depending on local electricity rates, available incentives, and system size.
Common Challenges and Solutions for Solar Adoption
While solar energy offers numerous benefits, homeowners often face several challenges when considering the transition. Understanding these obstacles and their solutions can help you make a more informed decision about going solar.

Challenges
- High upfront installation costs
- Roof suitability concerns (age, orientation, shading)
- Aesthetic impact on home appearance
- Navigating permits and utility requirements
- Finding qualified, trustworthy installers
Solutions
- Financing options, tax credits, and incentives
- Professional roof assessment and alternative mounting options
- Modern, low-profile panel designs and building-integrated options
- Working with installers who handle permitting process
- Researching certified installers with strong reviews and warranties
Addressing the Upfront Cost Barrier
The initial investment in solar panels remains one of the biggest hurdles for many homeowners. However, several financial options have made solar more accessible:
Solar Loans
Many financial institutions offer specialized solar loans with favorable terms. Monthly loan payments are often less than your previous electricity bill, creating immediate positive cash flow while you pay off your system.
Solar Leases/PPAs
These options allow you to install solar with little or no money down. You either lease the equipment or purchase the power produced at a rate lower than utility prices. While you won’t own the system, you’ll still benefit from reduced electricity costs.
Incentives and Rebates
Federal tax credits, state rebates, and local incentives can significantly reduce the net cost of your solar installation. These programs vary by location but can cover 30% or more of your system cost.
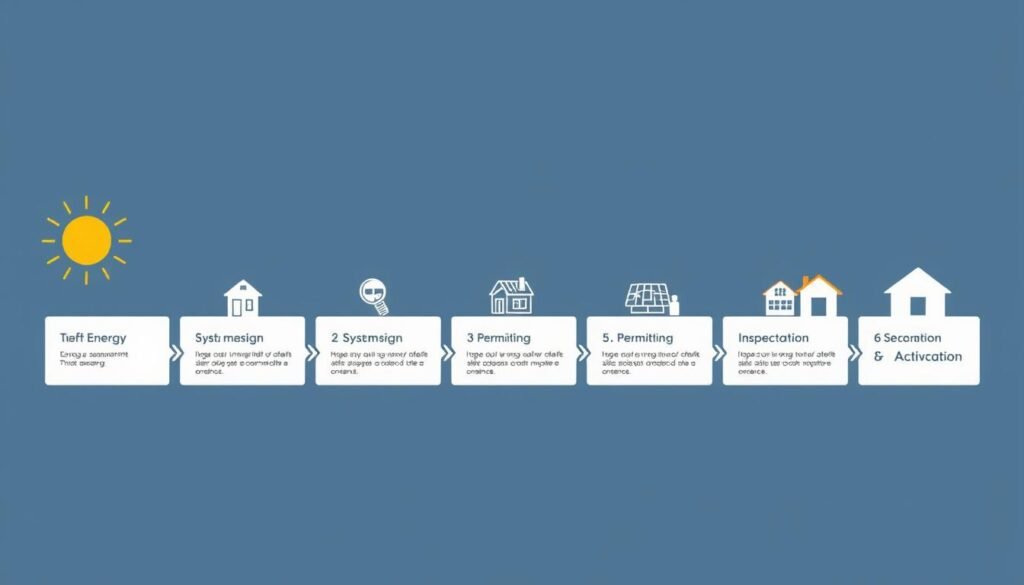
Steps to Transition to Solar Power
Making the switch to solar energy involves several key steps. This roadmap will guide you through the process from initial research to enjoying the benefits of your new solar power system.
-
Assess Your Energy Needs and Solar Potential
Begin by reviewing your electricity bills to understand your consumption patterns. Then evaluate your home’s solar potential by considering roof orientation, shading, and available space. Online tools like the PVWatts Calculator can provide preliminary estimates of solar production at your location.
-
Research Solar Incentives in Your Area
Investigate federal, state, and local incentives that can reduce your installation costs. The federal solar investment tax credit (ITC) offers a significant tax credit, while many states provide additional rebates or performance-based incentives. Your utility company may also offer net metering or other solar-friendly programs.
-
Get Multiple Quotes from Certified Installers
Contact several reputable solar installers to receive customized quotes for your property. Look for companies with proper certifications (like NABCEP), strong warranties, and positive customer reviews. Compare not just prices but also equipment quality, warranty terms, and projected energy production.

-
Select Your Financing Option
Decide how you’ll pay for your solar system. Options include cash purchase, solar loans, leases, or power purchase agreements (PPAs). Each has different implications for ownership, maintenance responsibilities, and long-term savings. Choose the option that best aligns with your financial goals and circumstances.
-
Complete Permitting and Interconnection
Your installer will typically handle the permitting process with local building departments and the interconnection application with your utility company. This step ensures your system meets all safety codes and can be properly connected to the grid.
-
Installation and Inspection
Once permits are approved, installation usually takes 1-3 days. After installation, your system will need to pass inspections by both the local building department and your utility company before it can be activated.
-
System Activation and Monitoring
After passing all inspections, your system will be connected to the grid and activated. Most modern systems include monitoring software that allows you to track energy production in real-time, helping you optimize your energy usage and verify system performance.
Essential Solar Energy Tips for Homeowners
Maximize the benefits of your solar investment with these practical tips that help optimize performance, increase savings, and ensure a smooth transition to solar power.

Optimize Panel Placement
South-facing roof sections (in the Northern Hemisphere) typically receive the most sunlight throughout the day. If south-facing installation isn’t possible, east and west orientations can still be effective. Avoid areas with significant shading from trees, chimneys, or neighboring buildings that could reduce energy production.
Improve Energy Efficiency First
Before installing solar, reduce your energy consumption by upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, improving insulation, and adopting conservation habits. A more efficient home requires a smaller, less expensive solar system to meet its energy needs.
Consider Battery Storage
Adding battery storage to your solar system allows you to store excess energy produced during the day for use at night or during power outages. While batteries add to the initial cost, they increase energy independence and can be especially valuable in areas with time-of-use electricity rates or limited net metering.
Maintain Your System
While solar panels require minimal maintenance, occasional cleaning and annual inspections help maintain optimal performance. In most climates, rain naturally cleans panels, but areas with heavy pollen, dust, or bird activity may require periodic cleaning with water and a soft brush.
Monitor Production Regularly
Use your system’s monitoring tools to track energy production and identify any performance issues early. Unexpected drops in output could indicate a problem that needs attention. Many monitoring systems offer mobile apps that make this process simple and convenient.
Time Your Electricity Usage
Shift energy-intensive activities like laundry, dishwashing, and electric vehicle charging to daylight hours when your solar system is producing electricity. This maximizes the use of your solar power and reduces reliance on grid electricity.
Beyond Panels: Other Ways to Embrace Green Electricity
Solar panels are just one component of a comprehensive approach to green electricity. Consider these complementary strategies to further reduce your environmental impact and enhance your energy independence.
Energy Storage Solutions
Battery systems like the Tesla Powerwall or LG Chem RESU store excess solar energy for use during peak rate periods or power outages. These systems are becoming more affordable and provide valuable backup power during grid failures. Some utilities even offer incentives for battery installation as they help stabilize the grid during high demand periods.

Smart Home Energy Management
Smart thermostats, energy monitoring systems, and automated appliances can optimize your energy usage to align with solar production. These technologies learn your habits and adjust consumption patterns to maximize the use of solar power when it’s available, further reducing your reliance on grid electricity.
Community Solar Options
If your home isn’t suitable for solar panels due to shading, roof orientation, or rental status, community solar programs offer an alternative. These shared solar facilities allow multiple participants to benefit from a single, centrally-located solar array, receiving credits on their utility bills for their portion of the generated power.
Green Power Purchasing
Many utilities offer green power purchasing programs that allow you to buy renewable energy credits (RECs) to offset your conventional electricity use. While not as financially beneficial as generating your own solar power, these programs support the development of renewable energy projects and reduce your carbon footprint.
Frequently Asked Questions About Solar Power
Here are answers to some of the most common questions homeowners have about transitioning to solar energy.
How long do solar panels last?
Most solar panels come with 25-30 year warranties and typically continue producing electricity for 30-40 years, though at slightly reduced efficiency in later years. The inverter (which converts DC power from panels to AC power for home use) generally needs replacement after 10-15 years. Many premium solar panels maintain over 80% of their original efficiency even after 25 years of operation.
Do solar panels work in cloudy weather?
Yes, solar panels continue to generate electricity on cloudy days, though at reduced capacity (typically 10-25% of their rated output). Modern panels use both direct and indirect sunlight to generate power. Even regions with frequent cloud cover, like the Pacific Northwest or parts of New England, can still benefit significantly from solar power. Germany, which receives similar sunlight to Alaska, has been a world leader in solar adoption.
How much roof space do I need for solar panels?
A typical residential solar panel is about 65 by 39 inches (5.4 feet by 3.25 feet) and produces around 300-400 watts. For a 6kW system, which is average for many homes, you’ll need approximately 15-20 panels, requiring about 300-400 square feet of roof space. The exact number depends on your energy needs, panel efficiency, and roof characteristics.
Will solar panels damage my roof?
When properly installed by qualified professionals, solar panels should not damage your roof. In fact, they can protect the portion of roof they cover from weather and UV exposure, potentially extending its life. Most installations use mounting systems that don’t penetrate the roof membrane, and all roof penetrations are properly sealed and flashed to prevent leaks. It’s recommended to install solar on a roof that has at least 10 years of life left to avoid the cost of removing and reinstalling panels during a roof replacement.
What happens with solar panels during a power outage?
Standard grid-tied solar systems automatically shut down during power outages as a safety measure to prevent sending electricity to the grid while utility workers are making repairs. To maintain power during outages, you’ll need either a solar system with battery storage or one with special “islanding” capability that can safely disconnect from the grid while continuing to power your home.
Can I install solar panels myself?
While DIY solar installation is technically possible, it’s generally not recommended for most homeowners. Professional installation ensures proper system design, safe electrical work, compliance with building codes, and qualification for incentives and warranties. Improper installation can lead to reduced efficiency, roof damage, fire hazards, and voided equipment warranties. Additionally, most utilities require professional certification before connecting to the grid.
Helpful Resources for Solar Energy Research
These trusted resources can help you learn more about solar energy and make informed decisions about transitioning to solar power for your home.

Solar Calculators
- PVWatts Calculator – Estimates energy production and cost savings for grid-connected PV systems
- EnergySage Solar Calculator – Personalized solar savings estimates based on your location and energy usage
- Solar-Estimate.org – Calculates system size, cost, and savings with local incentive information
Government Resources
- Department of Energy: Homeowner’s Guide to Going Solar – Comprehensive resource for residential solar information
- DSIRE Database – Comprehensive source for incentives and policies supporting renewable energy
- ENERGY STAR – Information on energy-efficient products and practices to complement solar installation
Industry Organizations
- Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) – Industry information and consumer resources
- Clean Energy Resource Teams – Community-based clean energy resources and case studies
- Solar Power World – News and information about solar technology and industry developments
Embracing Solar Power for a Sustainable Future
Solar energy represents one of the most accessible ways for homeowners to participate in the renewable energy transition while enjoying tangible financial benefits. By generating clean electricity from the sun, you not only reduce your monthly utility bills but also decrease your environmental impact and increase your energy independence.

As solar technology continues to advance and costs decline, the case for residential solar power grows stronger each year. Whether your primary motivation is environmental stewardship, protection against rising energy costs, or increasing your property value, solar energy offers a compelling solution that aligns personal benefits with global sustainability goals.
By following the steps outlined in this guide and utilizing the resources provided, you can confidently navigate the process of transitioning to solar power. The journey toward sustainable living begins with informed decisions about how we power our homes—and solar energy provides a bright path forward.
Every solar panel installed is a step toward a cleaner, more sustainable energy future—one rooftop at a time.





